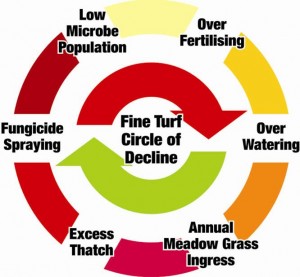
How can we ensure a consistently high performance bowling green that is economical to produce and maintain. There are 4 specific goals that we need to achieve to say that we have such a green:
How can we ensure a consistently high performance bowling green that is economical to produce and maintain. There are 4 specific goals that we need to achieve to say that we have such a green:
Green Speed; the actual surface pace that we can reasonably expect from the green on a regular basis.
Consistency; the ability of the green to replicate high performance throughout the day, week and season and also from season to season.
Predictability; the ability of the green and individual rinks to be set up for play of a reasonably predictable nature, time after time and over time.
Achievability; high performance must be not only physically achievable but also relatively easily achievable and for that the program we put in place must tick the following boxes; it must be:
Workable; with “in-house” labour and skills or with a financially sustainable amount of “bought in” labour and skills.
Sustainable in terms of its environmental, financial and infrastructural requirements.
Replicable time after time within the parameters defined above.
Minimum Input in terms of artificial fertilisers, chemicals and expensive bought in machinery or skills.
The goals we have set above require us to produce a very specific kind of green surface.